6T- How to Measure Ground Resistance and Optimize Grounding Grid
This course is suitable for engineers with a desire to understand the fundamentals of earthing resistance measurements. Presented details cover issues related to different measurement methods including two and three point measurement method, fall of potential method, touch potential measurements, ground grid integrity measurements, etc. Upon successful completion engineers will be able to understand theory and practical ground resistivity measurement methods which will provide a solid understanding for further engineering work.
In “How to Measure Ground Resistance and Optimize Grounding Grid” course, you'll learn...
- -Effect of ground electrode size and depth on resistance
- -Effect of soil resistivity on ground electrode resistance
- -Factors affecting soil resistivity
- -Effect of ground electrode depth on resistance
- -Ground resistance measurements
- -Two-Point ground resistance measurement method
- -Three-Point ground resistance measurement method
- -Fall-of-potential ground resistance measurements method
- -Measuring resistance of ground Electrodes (62% Method)
- -Multiple electrode system
- -Soil resistivity measurements (Four-Point measurement)
- -Touch potential measurements
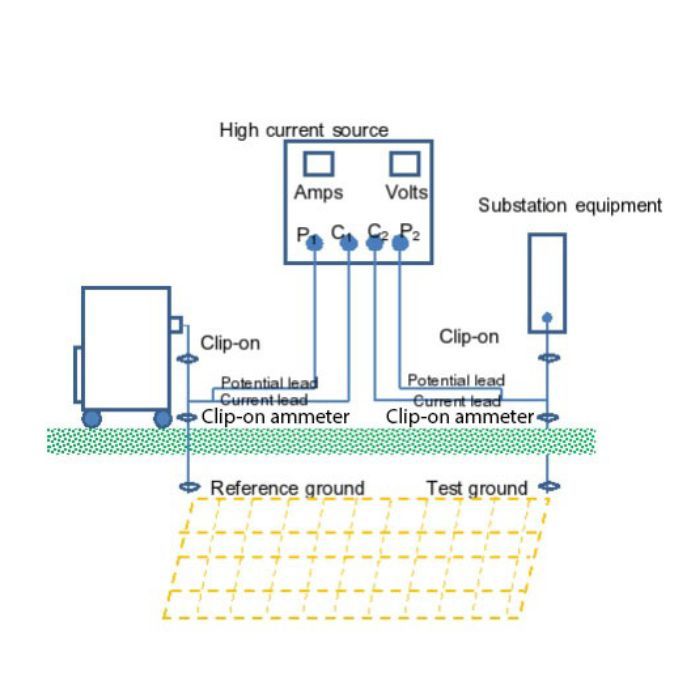
- -Clamp-On ground resistance measurement
- -In-Field measurement
- -Ground grid integrity measurements
- -PV system characteristics and potential hazards
- -Relevant safety standards and codes
- -Possible injuries and basic first aid concepts
Overview The term ground is specified as a conducting link by which a circuit or device is connected to the earth. The link is used for establishing and keeping as closely as possible the potential of the ground on the circuit or device linked to it. A ground consists of a grounding conductor, a bonding connector, its grounding electrode(s), and the soil which is in contact with the electrode. Grounds have few basic protection applications. For natural phenomena, such as lightning, grounds are used to secure a discharge path for the current to decrease shock hazard to staff and to avoid damage to equipment and property.
For induced potentials due to failures in electric power systems with earth returns, grounds help in ensuring quick operation of the protection relays by giving low resistance fault current paths. This allows clearing the induced potential as fast as possible. The earth has to drain the induced potential before staff is injured and the power or communications equipment is damaged. In ideal conditions, to keep a reference potential for instrument safety, to protect against static electricity, and limit the equipment earth voltage for operator safety, an earth resistance needs to be 0 Ω. However, in reality, this value cannot be reached. Also, low earth resistance is demanded by NEC, OSHA, and other electrical safety codes and regulations. This course is suitable for engineers with a desire to understand the fundamentals of earthing resistance measurements. Presented details cover issues related to different measurement methods including two and three point measurement method, fall of potential method, touch potential measurements, ground grid integrity measurements, etc. Upon successful completion engineers will be able to understand theory and practical ground resistivity measurement methods which will provide a solid understanding for further engineering work.
| Objetivos de aprendizaje | This course teaches the following specific knowledge and skills:
|
|---|---|
| Horas de Contacto | 6 Horas |
| Cursos CIAPR | CURSO TECHNICO |
| Instructor | Velimir |
| Dispositivos | Desktop, Tablet, Mobile |
| Idioma | English |

IACET ACCREDITED PROVIDER
|
Self Learning Solutions LLC es una empresa con más de 14 años de experiencia en este mercado. En Self Learning Solutions estamos orgullosos de haber obtenido la acreditación IACET para nuestra organización, junto con las aprobaciones necesarias para comercializar nuestros productos en todo Estados Unidos. Self Learning Solutions está acreditado por la Asociación Internacional para la Educación y Formación Continua (IACET). Self Learning Solutions cumple con el estándar ANSI / IACET, que es reconocido internacionalmente como un estándar de excelencia en las prácticas de instrucción. Como resultado de esta acreditación, Self Learning Solutions está acreditada para emitir la CEU IACET. |
Requisitos del sistema de SLSTECH
Para ejecutar nuestro sistema de manera eficaz, como mínimo, debe utilizar los componentes del sistema que se enumeran en esta página. Si no lo hace, es posible que el sistema aún funcione pero que se pierda alguna funcionalidad. Las configuraciones internas de los entornos de IT del lugar de trabajo también pueden restringir la funcionalidad de nuestro sistema. El acceso al contenido puede verse afectado, al igual que la posibilidad de subir archivos. También pueden aplicarse limitaciones de tamaño de archivo. Los lugares de trabajo también pueden tener versiones anteriores de software, y nuestro sistema puede no funcionar bien con estos.
Sistema operativo
-
Recomendado: Windows 7, 10, Mac OSX Sierra, iPad IOS10
Velocidad de Internet
-
Use una conexión de Internet (broadband connection) (256 Kbit / seg. o más rápida, esto le permitirá ver videos y presentaciones en línea) a través de un módem inalámbrico USB, ADSL, T1 / T2, fibra óptica o cable.
-
El acceso telefónico será mucho más lento y no lo recomendamos para usar nuestro systma.
Navegadores de Internet
Los navegadores compatibles incluyen:
-
Google Chrome 32 bit versión 50 o posterior (recomendado para una compatibilidad óptima, esto se ha probado exhaustivamente en Windows)
Safari 10 o posterior (recomendado para una compatibilidad óptima, esto se ha probado exhaustivamente en Mac)
Tenga en cuenta que los complementos y las barras de herramientas pueden afectar el rendimiento de cualquier navegador.
-
No se recomienda MS Internet Explorer
Configuraciones
Recomendamos que se habilite lo siguiente:
-
Cookies
-
Ventanas emergentes "Pop-ups" (tanto en el navegador de Internet como en el software de seguridad)
-
Javascript
-
Le recomendamos que utilice la última versión de Adobe Flash Player.
Software
-
Le recomendamos que utilice la última versión de Adobe Acrobat Reader.
-
Para ver todos los recursos cargados en Hazmat Authority, es probable que necesites tener instalado Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint) o un equivalente (por ejemplo, Open Office, Viewer).
Seguridad
Con todos los "firewalls", asegúrese de habilitar la carga de archivos.






Validate your login
Registrarse
Crear una nueva cuenta